
You will see them very frequently while checking memory usage in Linux. The units have shorthand notations or symbols. So, computers use powers of 2 to represent the amount of storage or memory. But, for computers, it’s easier to calculate in powers of 2 (binary numeral system). For us humans, it’s easy to calculate in powers of 10 (decimal numeral system) as we have 10 fingers. But, kibibyte, mebibyte, gibibyte, tebibyte, and pebibyte are powers of 2 bytes. Notice that kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, terabyte, and petabyte are powers of 10 bytes. Now that you know the computer storage units, you should be able to convert from one unit to another very easily. In terms of bytes, the computer storage units are as follows. Pebibyte: 1,024 tebibytes form a pebibyte.Tebibyte: 1,024 gibibytes form a tebibyte.Gibibyte: 1,024 mebibytes form a gibibyte.Mebibyte: 1,024 kibibytes form a mebibyte.Petabyte: 1,000 terabytes form a petabyte.Terabyte: 1,000 gigabytes form a terabyte.Gigabyte: 1,000 megabytes form a gigabyte.Megabyte: 1,000 kilobytes form a megabyte.Bit: The smallest unit of computer storage is a bit.The computer storage units are given below. I will explain them in this section.Īll the computer storages use the same unit. In this article, you will see me using the terms kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, kibibytes, mebibytes, gibibytes, and so on. In this article, I am going to show you some of the most common ways to check memory usage on Linux.

There are many tools to check memory usage in Linux. You can diagnose many Linux problems if you can monitor RAM usage of your Linux system. In the worst case, your entire system will hang and become unusable.Ĭhecking RAM usage is one of the most important tasks in Linux. You may not be able to start any new programs. The running programs of your computer may hang or stop. Without enough free RAM, your computer won’t function properly. Unfortunately, RAM is very expensive and limited. That’s why all the programs use RAM for storing cache data. Thus, the data access latency is very small compared to storage devices such as HDD or SSD. As RAM is closer to the CPU of the computer, the CPU has direct access to RAM. RAM is very fast and it’s closer to the CPU (Central Processing Unit) of the computer. The programs you run on your computer store small bits of information in the RAM so that it can access it when needed as fast as possible. The -l option displays detailed high and low memory size statistics.Memory or RAM (Random Access Memory) is very important for a computer.
#Check free memory linux update
The -s option with number, used to update free command at regular intervals.Ħ. Free command with -t option, will list the total at the end.ĥ. Free command with option -g, display the size of memory in gigabytes.Ĥ. Free command with option -m, display the size of memory in megabytes.ģ.

If the -o option is not specified, free subtracts buffer memory from the used memory and adds it to the free memory reported. The -o switch disables the display of a “buffer adjusted” line.The -t switch displays a line containing the totals.
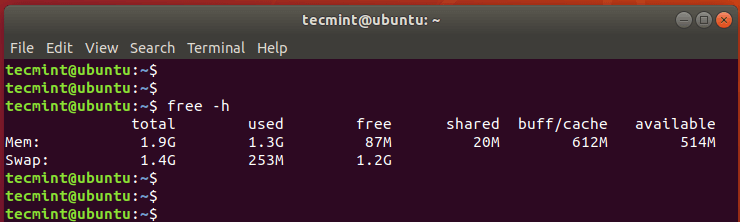
The -b switch displays the amount of memory in bytes the -k switch (set by default) displays it in kilobytes the -m switch displays it in megabytes.
#Check free memory linux for free


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
